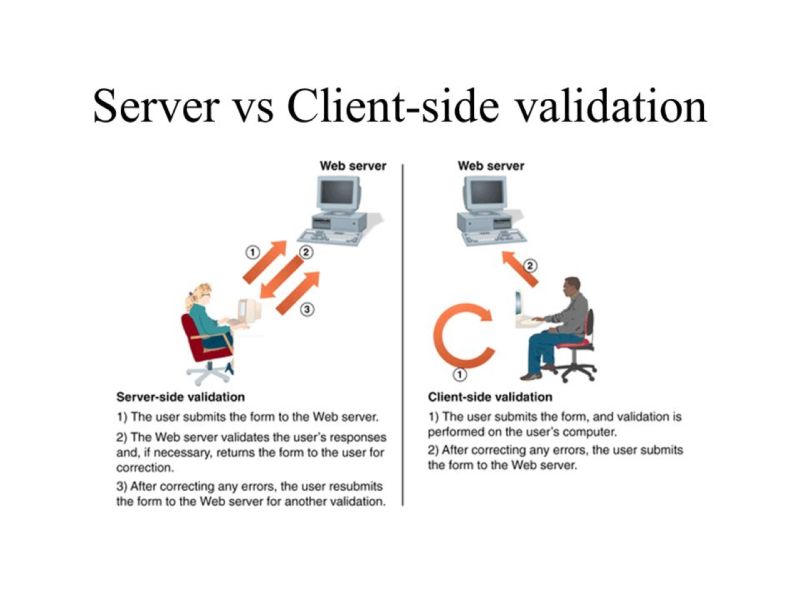
Client-Side vs. Server-Side Validation: A Comparative Analysis
In web development, both client-side and server-side validation are crucial for ensuring data integrity, security, and a seamless user experience. Let’s break down the key differences and why both are essential.
Client-Side Validation
What is it? Client-side validation occurs on the user’s device, typically using JavaScript. It checks input data before it’s sent to the server.
Advantages:
- Immediate feedback: Users receive instant error messages, improving the user experience.
- Reduced server load: Valid data is filtered before being sent to the server, reducing unnecessary processing.
- Faster response times: Users don’t have to wait for a server response to know if their input is valid.
Disadvantages:
- Security risk: It can be bypassed by users who disable JavaScript or manipulate the HTML form.
- Limited validation capabilities: Complex validation rules may be difficult to implement solely on the client-side.
Server-Side Validation
What is it? Server-side validation occurs on the web server. It re-checks the data received from the client to ensure its accuracy and security.
Advantages:
- Enhanced security: Protects against malicious attacks and invalid data.
- Reliable validation: Ensures data integrity, even if client-side validation is bypassed.
- Customizable rules: Allows for more complex validation rules and business logic.
Disadvantages:
- Slower response times: Users may experience delays while the server processes the data.
- Increased server load: The server needs to process and validate each request.
Best Practices: Combining Both Approaches
For optimal security and user experience, it’s recommended to use a combination of both client-side and server-side validation:
-
Client-Side Validation:
- Provide immediate feedback to users.
- Improve user experience by preventing invalid submissions.
- Reduce unnecessary server requests.
-
Server-Side Validation:
- Ensure data integrity and security.
- Protect against malicious attacks and invalid input.
- Handle complex validation rules and business logic.
Example:
Consider a form with a required email field.
- Client-side: JavaScript can check if the field is empty and if the email format is valid.
- Server-side: PHP can re-validate the email format, check if the email address is already in use, and perform additional security checks.
By combining these approaches, you can create a robust and secure web application that delivers a seamless user experience.